
AI Agents: Turning Imagination into Reality
After sharing our GenAI thesis and the 16 fields we are particularly excited about in AI, we’re delving into one of the most interesting trends in the era of capabilities unlocked by GenAI: AI agents, and, specifically, human simulating agents.
AI agents are software entities that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions independently without human supervision. They are the closest approximation we have today to the vision of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), replicating a broad range of human cognitive abilities, including perception, reasoning, planning, learning, and adapting to new situations without dedicated preparation.
AI Agents Add Value Across the Board
The AI agents space can be divided into several key subspaces and categories, some of which we have already started investing in. One agent can have multiple overlapping functionalities and several interfaces simultaneously:
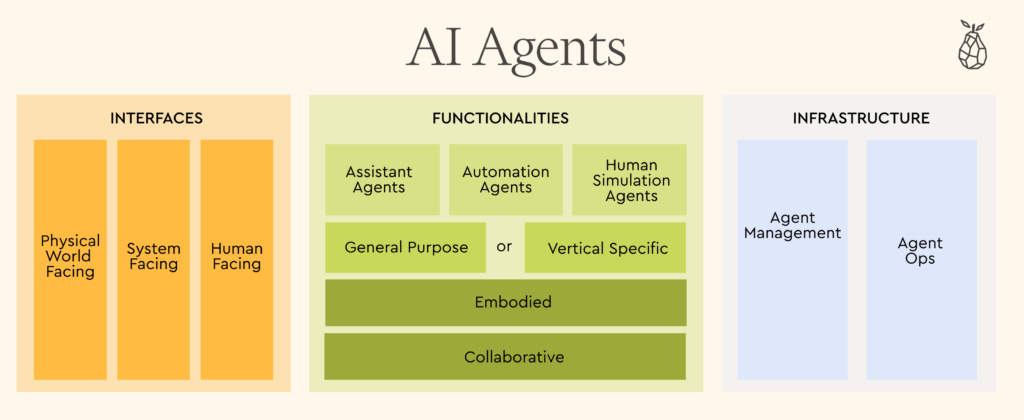
AI Agents with Specific Functionalities
- Human-simulating agents: These agents simulate human behavior and thoughts based on a given profile or need. These transformative approaches can be applied to various use cases, from companions that fight loneliness, to agents with demographic traits, beliefs, and preferences that help predict trends like election results or consumer adoption more quickly, cheaply, and accurately. See more in our section on Human Simulating Agents below.
- Assistant agents: These agents can handle a wide range of tasks, from running an online search, or playing a song upon voice request (e.g. Siri and Alexa), to scheduling a doctor’s appointment and maintaining a detailed to-do list, as Ohai.ai and Martin do.
- Automation agents: These agents connect two machines, identify gaps and repetitive processes, and create automated workflows to enhance them. For example, Orby AI, backed by Pear, automates workflows for enterprises in minutes, improving team efficiency by over 60%.
- General purpose agents: While very broad and challenging to build effectively, these agents can complete multiple tasks across different verticals and complexity levels. Key players in this space include BabyAGI, AgentGPT and Personal AI, which offer solutions for various problems through their agents.
- Vertical agents: Highly skilled in specific fields such as healthcare, marketing, gaming, legal, and more, these agents excel in their respective areas. A promising code generation agent and engineering co-pilot is Devin, built by Cognition AI, which enables engineers to plan and execute complex engineering tasks.
- Embodied agents: Embodied agents operate on edge devices such as IoT devices, robots, and drones, as navan.ai does. They enable smarter and more independent decision-making and actions, aiming to improve smart home systems, agricultural practices, defense, and more.
- Collaborative agents: These agents can interact effectively with other agents, learn from each other, and cooperate to improve their performance and execution over time. Relevance AI is building such solutions to increase team productivity.
Agents with Defined Interfaces
- Human Facing Agents: interact with humans through text, audio, video, etc., just like Google Astra does to help people navigate their surroundings.
- System Facing Agents: Interact with machines and systems through APIs, scripting, and data.
- Physical world facing agents: interact with the physical world, learning and interacting with it through robots, drones, and automotive, as Tesla autopilot and Weymo.
Agents Infrastructure
Agents infrastructure will include ops layers that encompass memory, compute and data infrastructure. Additionally, new agent management platforms will emerge, enabling building, orchestration, observability, and monitoring. Companies like Dust and AgentOps aim to offer these solutions to help agents and their operators achieve their full potential.
Human Stimulating Agents: Revolutionizing Customer Support, Trend Predictions, and More.
Human simulating agents allow us to leverage AI to learn from and predict human behavior in different scenarios. There are two broad categories of Human Simulating Agents:
Support agents
- Assistants: As mentioned above, AI assistants can simulate human behavior while supporting us. For example, they can order and adjust our grocery lists based on our historical needs and preferences, declutter our email inboxes, and respond in our unique writing styles. They will interact with us in natural language, as if we were asking for help from a close friend, helping us manage our busy lifestyles.
- Customer support: AI agents in the customer support space will become more sophisticated, providing relevant and satisfying support that saves man-hours, reduces customer frustration, and cuts costs for customer-facing companies. Sierra, Crescendo and yellow.ai are already on a mission to transform the customer support experience using AI agents.
Human persona agents
- Trend predictions: Agents will simulate people with specific demographic contexts, traits, and perspectives to predict the adoption of new consumer products, as Keplar and subconscious.ai do, create the most effective personalized marketing content, predict election results, and more.
- Companions: AI agents can become companions with personality and relationship history, remembering key moments in our lives, fighting loneliness, and offering initial mental health support if needed. For example, Replika and Kindroid provide engaging relationships with customizable AI companions that users can interact with through text and voice.
Building in this space?
If you are building in the agents space, reach out to us (Arash or Arpan). We would love to discuss your vision and explore how we can support your journey.
Acknowledgements: I’d like to thank Pear AI Fellow Libby Meshorer for significant contributions to this post as well as Pear team members Arpan Shah, Jill Puente, and Lucy Lee Duckworth for contributing.